Climate change is no longer an abstract concept or a future problem that can just be brushed aside to worry about later. It is real, and it is a pressing challenge that demands our immediate attention. As Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions continue to increase and global temperatures rising as a result, the adverse effects on our planet have become more pronounced than ever.
In recent years, the need to step up efforts in combating climate change has become more evident. This has led organizations around the world to adopt various mitigation steps, commitments, and measures to reduce the adverse effects of climate change & help preserve our planet.
At the heart of this challenge lies the critical concept of net zero emission. But what does it actually mean? And why has it become the focal point of climate action?
In this blog post, we will focus on net zero emission, breaking down its significance and implications for businesses. We will discuss the pathways & solutions that can lead us towards a net zero future and also look at the difference between real zero and net zero emissions.
The reality of climate change
Over the past century, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have significantly increased the concentration of GHGs in the atmosphere. As a result, the Earth’s average temperature has risen steadily, leading to a series of devastating consequences.
Since 1880, average global temperatures have risen by 2.2 degrees Fahrenheit, with the most substantial changes occurring in the late 20th century. Land areas have experienced more significant warming compared to the sea surface. The Arctic region has warmed the most, with temperatures soaring by over 4 degrees Fahrenheit since the 1960s. These factors have also led to a noticeable shift in temperature extremes across the globe.
This warming stands unparalleled in recent geologic history. A famous illustration, initially published in 1998 and commonly known as the hockey stick graph, shows how temperatures remained fairly flat for centuries before taking a sudden and pronounced upward turn.
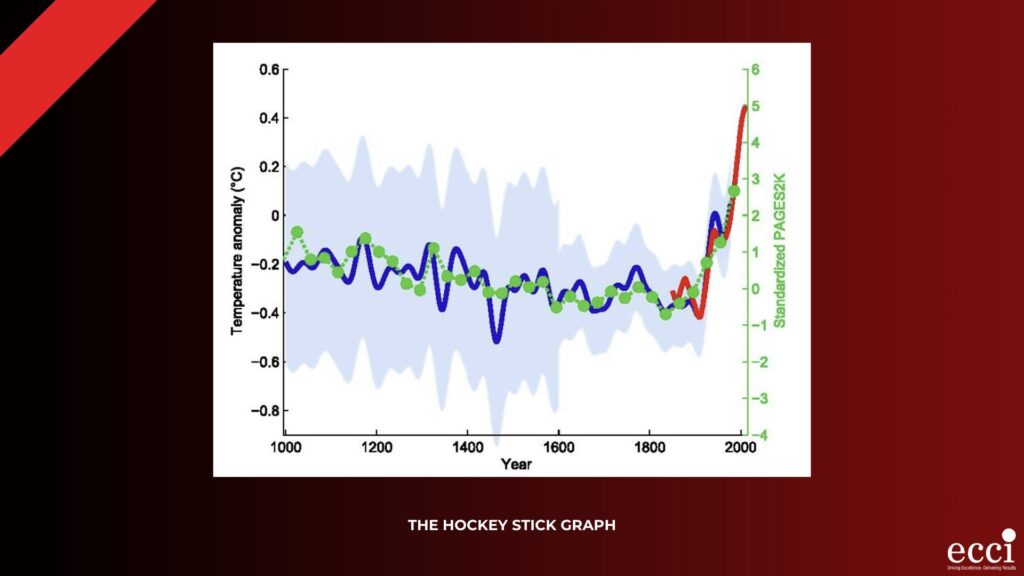
This graph was created based on data from tree rings, ice cores, and other natural indicators. And it clearly indicates that Earth is currently experiencing higher temperatures than at any point in at least 1,000 years and potentially even much longer.
The consequences of this rise in temperature can be seen everywhere. Natural disasters like hurricanes, droughts, floods, and wildfires are becoming more frequent and intense, wreaking havoc on communities and ecosystems. The polar ice caps are melting at an alarming rate, contributing to rising sea levels that threaten coastal regions and low-lying islands. Moreover, ocean temperatures are increasing, causing coral bleaching and disrupting marine ecosystems.
The impacts of climate change are not just limited to the environment, they also extend to social and economic spheres. Vulnerable communities, particularly those in developing countries, bear the brunt of climate-related disasters, facing displacement, food insecurity, and water scarcity. Additionally, businesses are increasingly facing supply chain disruptions, increased insurance costs, and potential financial losses due to climate-related risks.
Impacts like these, among numerous others, will only become more severe if we don’t take decisive action to stop the GHG emissions.

What is net zero emission? – The 1.5C challenge
Net zero emission refers to achieving an overall balance between the amount of GHGs emitted into the atmosphere & the amount removed from it. In simpler terms, it means reducing GHG emissions to as close to zero as possible and removing any remaining emissions through actions like planting trees or using technologies to capture and store carbon.
To put it into perspective, imagine a scale. On one side, we have GHG emissions released from human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, etc. On the other side, we have actions that absorb or reduce these emissions, like afforestation, reforestation, and carbon capture technologies. The goal is to achieve a balance between these two sides, resulting in net zero emissions.
Now, why is net zero emission so crucial? In order to address the urgency of the climate change challenge, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has set a daunting yet necessary target – limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Achieving this goal is commonly called ‘The 1.5C challenge’. This threshold is seen as critical to avoid the worst impacts of climate change and to protect vulnerable ecosystems and communities. And to stay within the 1.5C limit, we must achieve net zero emissions on a global scale by 2050.
Why pursue net zero?
As we have seen in the previous section, in order to limit the global temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, it is imperative for organizations and governments to take steps to decrease GHG emissions significantly and achieve net zero by 2050.
Apart from this, there are several other compelling reasons why businesses must wholeheartedly embrace the goal of achieving net zero emissions. They are:
a. Reducing business risks
Climate change poses significant risks to businesses across all sectors. From supply chain disruptions due to extreme weather events to increased insurance costs and reputational damage, failing to address emissions can expose companies to avoidable risks. By embracing net zero strategies, businesses can build resilience, prepare for climate-related disruptions, and ensure business continuity.
b. Lower transitional and operating costs
Because of urgent climate action, many companies will soon have to replace older, less efficient systems with more sustainable alternatives. Companies can get ahead of this by taking steps toward net zero emissions before rising demands drive up prices.
c. Improved health
The transition to renewable energy sources like wind and solar power can have significant health benefits by reducing air pollution. Burning fossil fuels to produce energy releases harmful pollutants into the air, causing severe respiratory & cardiovascular health issues. By moving to renewable energy sources, we can reduce the number of illnesses & deaths caused by air pollution.
d. Adapting to changing regulatory requirements
As the world acknowledges the urgency of addressing climate change, governments are implementing stricter regulations and policies to curb emissions. Businesses that proactively pursue net zero will be better positioned to adapt to changing regulatory requirements and avoid potential penalties.
e. Enhancing brand reputation
Consumers and investors are becoming increasingly conscious of environmental issues. By committing to net zero emissions, businesses can enhance their brand reputation, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and appeal to sustainable-focused investors.
f. Gaining market advantage
An increasing number of consumers not only want to support sustainable businesses but are also willing to pay a premium for sustainable goods and services. Companies that commit to net zero thus have an enormous advantage over companies that either don’t pursue net zero or greenwash their efforts.

g. Meeting stakeholder expectations
Shareholders, employees, and communities increasingly expect businesses to take meaningful action on climate change. Embracing net zero demonstrates a commitment to responsible corporate citizenship and strengthens stakeholder trust in the company.
h. Appealing to young talent
Young professionals are typically more progressively minded on environmental matters. Consequently, workplaces that emphasize sustainability are more likely to attract and retain young talented employees who value a commitment to combating climate change by reducing emissions.
i. Leading the way
Businesses that pursue net zero emissions become leaders in sustainability and play a vital role in driving broader societal change. By setting ambitious targets and showcasing the feasibility of net zero, they inspire others to follow suit and contribute to a collective climate solution.
Pathways and solutions for net zero emissions
Achieving net zero carbon emissions is not going to be easy and will require a range of solutions applied together and a combined effort from all sectors of society to reach the goal.
It requires a massive transformation of our energy systems, transportation, land use, and industrial practices and also demands a shift in mindsets and policies to prioritize sustainability over short-term gains.
Now let’s explore some key strategies that businesses can adopt to embark on their journey towards achieving net zero emissions and contribute to the global mission of combating climate change.
A. Renewable energy adoption
At present, the energy sector is responsible for roughly three-quarters of GHG emissions, making it a key player in averting the most severe impacts of climate change. By replacing polluting coal, gas, and oil-fired power plants with renewable energy sources like wind or solar, companies can significantly reduce carbon emissions and contribute towards the collective goal of transitioning to a net zero world.

B. Carbon removal projects
Organizations can compensate for their unavoidable GHG emissions by investing in projects to remove or reduce an equivalent amount of carbon from the atmosphere. These projects could include activities like afforestation and reforestation, as well as investments in technologies that capture and store carbon.
C. Circular economy practices
Companies need to embrace circular economy principles, such as product design for longevity, recycling, and waste reduction. This can minimize emissions associated with resource extraction, manufacturing, & disposal and ensures more sustainable use of materials.
D. Shifting to electric vehicles
Transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs) and supporting sustainable transportation options can significantly cut down emissions from the transportation sector. Companies can encourage the adoption of EVs among their employees and invest in EVs themselves and use them for transporting and delivering goods.
E. Improving energy efficiency
Businesses need to focus on Improving energy efficiency within operations and supply chains. By conducting comprehensive energy audits and implementing energy-saving measures, they can optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and cut down GHG emissions effectively.
F. Setting science-based targets (SBTs)
To ensure businesses align their efforts with global climate goals, they should start setting science-based emission reduction targets. By adhering to scientifically informed targets, companies can track their progress more effectively and make meaningful contributions to the fight against climate change. Learn more about SBTs and how to get started on the SBT path here.
G. Financial incentives & investments
Financial institutions and investors play a crucial role in supporting the transition to net zero. By offering incentives for sustainable projects and investing in green technologies, they can drive the transformation towards a net zero future.
H. Carbon capture & storage
Carbon capture technologies can capture & store carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants. These technologies can help in reducing emissions from sectors where direct emissions reductions are more challenging.
The difference between real zero and net zero
The terms “real zero” and “net zero” often surface in discussions about emissions reduction and sustainability. While they both have the same overarching goal of reducing the adverse effects of climate change on our planet, they are actually two different approaches, and understanding the difference between both is critical to grasp the true impact of efforts to combat climate change.
Real zero refers to achieving absolute emissions reductions to the point where a company or an industry emits no GHGs whatsoever. This involves eliminating all carbon dioxide and other GHG emissions at the source, leaving no traces of these gases in the atmosphere. Achieving real zero is a monumental challenge and often requires transformative changes, such as transitioning to 100% renewable energy, adopting carbon capture and storage technologies, and optimizing industrial processes to be carbon-neutral.
Net zero, on the other hand, is a more flexible approach that allows for some emissions to remain as long as they are offset by an equivalent amount of carbon removals or reductions elsewhere. In this approach, a company or sector can still emit a certain amount of GHGs, but they must ensure that the emissions are balanced out by actions that remove or offset an equal amount of emissions from the atmosphere. This can include measures such as afforestation (planting trees to absorb carbon), investing in carbon capture projects, or supporting renewable energy initiatives that displace fossil fuel usage.
Conclusion
The reality of climate change demands urgent and collective action. Governments, businesses, and individuals must come together to reduce GHG emissions, transition to renewable energy sources, and adopt sustainable practices.
Now, armed with knowledge and a shared purpose, we find ourselves on the brink of transformation, where the choices we make today will echo through generations to come. Embrace the path of sustainability, adopt innovative strategies, and together, let us forge ahead on this collective journey toward a greener and more sustainable future. Learn more about why sustainability is crucial among businesses and the key elements of a sustainable business here.
Stay tuned for the third part in this blog series, Future-proofing Through Sustainable Business – Part 3: Science-Based Targets (SBT) Initiative, Net Zero Standard, And Net Zero Targets, where we’ll delve deeper into critical aspects of sustainability, specifically focusing on the Science-based Targets (SBT) Initiative, Net Zero Standard, & Net Zero Targets.
If you need assistance in taking proactive steps toward sustainability and becoming a carbon-neutral organization, reach out to us at ECCI. Our team of experts can help by identifying carbon emissions sources, conducting carbon footprint assessments based on ISO 14064 (GHG Emissions) standards, and determining potential areas of emission reduction in your organization. Visit our webpage for more information on how we can help you.